Detect and Treat Oral Chlamydia: Important Information About Throat Infections
Oral Chlamydia: Not a Sore Throat
Let’s clear one thing up; it is possible to get chlamydia in the throat. This is usually only possible if someone is giving oral sex to another person already infected with chlamydia. Oral chlamydia is not as common as genital chlamydia, but it is possible.
Chlamydia is a common and curable sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by the bacteria chlamydia trachomatis. Chlamydia can affect the cervix in women as well as the urethra and rectum in both men and women. The bacteria target the cells of the mucous membranes which aren’t covered by skin. These include the surfaces of the vagina, urethra, lining of the eyelid, and, the topic of this blog post, the throat.
When chlamydia occurs in the throat, it is considered a mouth infection. If there are symptoms (typically, there are none), they make it look a lot like tonsilitis. The infection causes white spots to appear in the back of the throat and can make it painful to swallow.
Preventing Oral Chlamydia: Tips for Keeping Your Mouth Infection Free
How do you get chlamydia in the mouth? When oral sex is performed on infected genitals, the giver is at risk of contracting chlamydia in the throat. Oral sex involves using the mouth, lips, or tongue to stimulate the penis, vagina, or anus of a sexual partner.
The risk of getting an STD from oral sex depends on things like the particular STD, the sexual activity performed, and how common the STD is in the population to which the sex partners belong. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), the risks of getting chlamydia in the throat increase if:
- You are performing oral sex on a male that has an infected penis.
- You are performing oral sex on a female that has an infected vagina or urinary tract.
- You are performing oral sex on a male or female that has an infected rectum.
The opposite is also true. The risks of getting genital chlamydia are increased if:
- You are receiving oral sex on the penis from a partner with chlamydia in the throat.
- You are receiving oral sex on the vagina from a partner with chlamydia in the throat can result in chlamydia of the vagina or urinary tract.
- You are receiving oral sex on the anus from a partner with chlamydia in the throat also might result in chlamydia in the rectum.
The infection can also be transferred from your fingers to other parts of your body, such as your eyes, nose, or mouth. Aside from sexual activities that easily spread chlamydia, there are a few other factors that will further increase your chances of getting this mouth infection. Chlamydia in the mouth symptoms can show up quickly.
The CDC states having poor oral health that results in tooth decay, gum disease (bleeding gums), or oral cancer increases the chances of acquiring the infection. This is due to a lowered immune system not being able to fight off both the oral hygiene infections and the invading chlamydia. If you have questions about chlamydia throat symptoms, feel free to give us a call.
Secure and Confidential
STD testing services
The fastest results possbile - available in 1 to 2 days
Is oral chlamydia a common thing?
If you think that neither you nor your partner belong to a population where chlamydia can spread, think again.
In the United States, there are over 1.5 million cases of chlamydia reported each year. However, the CDC estimates that at least 3 million actually occurred. Why the disparity in the numbers? In a survey done in 2013, only 30% of sexually active people from 15-25 reported testing the previous year.
Remember the saying, “If you sleep with one person, you’re also sleeping with the five other people they’ve slept with, and the five other people each of those people have slept with.” The spider web never ends. This means that that person from the New Year’s party in 2016 that your partner’s first partner’s partner slept with, ended up (probably unknowingly) giving you and the next person you sleep with an STD. Imagine what the number of cases of chlamydia in the U.S. actually is if people tested for STDs as often as they should.
Many people believe that only those who “have a risky sex life” are likely to get STDs. The truth is anyone sexually active at all is at risk to contract an STD.
Of all the groups, teens and young adults have the highest rates of infection. The most common bacterial STD is chlamydia.
If we could remove the stigma attached to STD testing, we’d all be much more likely to get tested. The United States would be able to do a little better in sexual health education, slow down the rates of STDs, and catch up with the rest of the developed world.
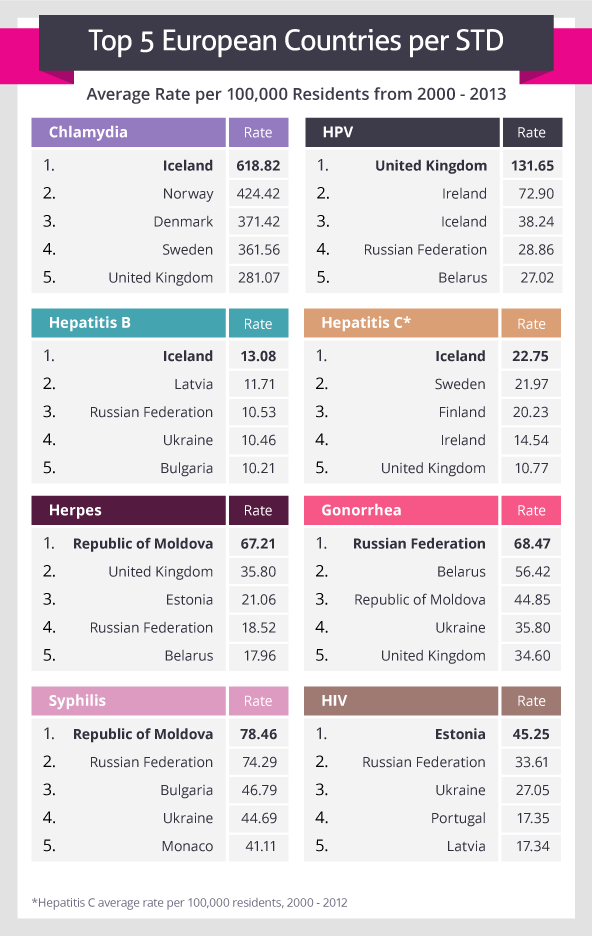
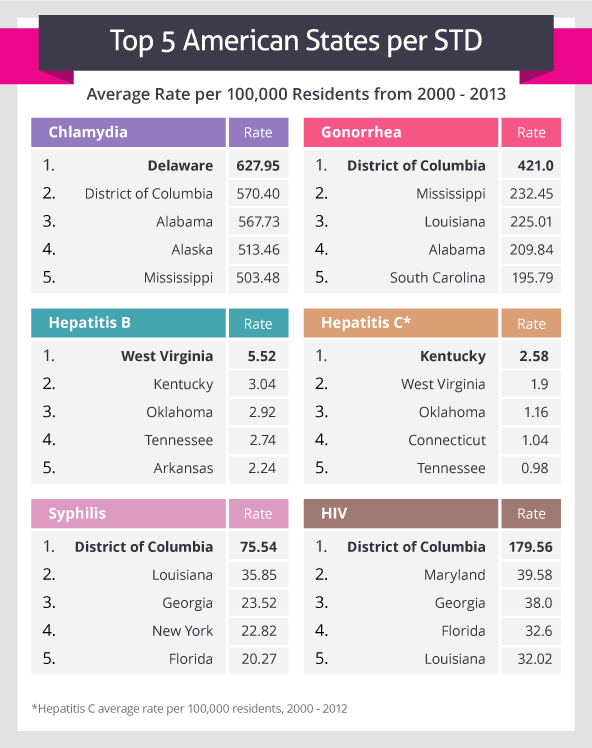
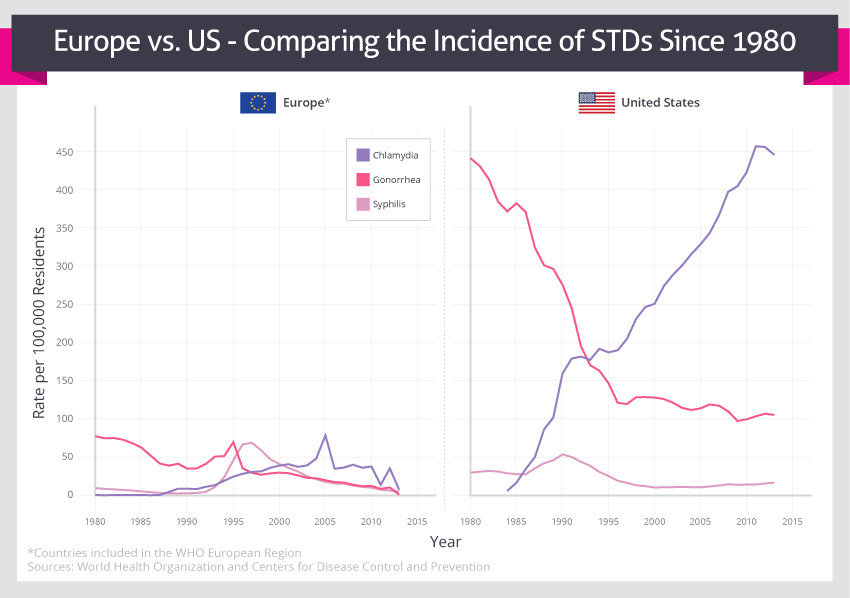
Credit: Superdrug
Chlamydia Throat Symptoms

Oral chlamydia infections affect the cells lining the throat. Most people with an oral chlamydia infection experience no symptoms, which leaves many unaware that they are infected. A true confirmation of oral chlamydia is only detected with testing.
For those that do experience symptoms, the most common symptom is a sore throat which lasts for several days. This discomfort can come and go, or it can be continually bothersome. Forget about drinking anything to make it better; just swallowing hurts too. A sore throat caused by chlamydia may be accompanied by a low-grade fever and swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
Some other possible chlamydia throat symptoms are:
- Painless sores in the mouth
- Lesions similar to cold sores around the mouth
- Tonsillitis
- Redness with white spots resembling strep throat
- Scratchy, dry throat
The possible chlamydia throat symptoms of genital chlamydia are:
- Potentially bloody discharge from the vagina or penis
- Burning feeling when urinating
- Painful or swollen testicles
- Rectal pain
Diagnosis & Treatment
Testing for oral chlamydia is usually done by swabbing the throat. After the diagnosis and confirmation, chlamydia can be cured with prescribed antibiotics. In order to avoid passing the STD to your partner and in turn giving yourself chlamydia again later, you should abstain from sex for the 7 days you are on antibiotics.
If caught early enough, chlamydia is easy to cure. The longer you go without treatment, the more likely it will go from mild to severe. Once it becomes severe, it can cause serious reactions in the body and make the healing process difficult, and, often times, the damage is irreversible.
If chlamydia in the throat is left untreated for too long:
STDs are not one of those illnesses that will just figure itself out. Not only will you spread chlamydia if you continue to have sex without treatment, but you can end up with some serious complications on your hands. There is a possibility that the chlamydia throat symptoms can get much worse.
Chlamydia can cause reproductive complications in women. It can spread to and infect the uterus and fallopian tubes, resulting in infertility, miscarriage, premature birth, and stillbirth.

If the pregnancy reaches full term, there can be complications in newborns as well as the postpartum mother when chlamydia has gone untreated. Half of the newborns get conjunctivitis (chlamydia in the eye), and they can also get urethritis. Mothers can get nose, throat, lung, and/or ear infections.
In men, a progressed chlamydial infection can result in urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), inflammation of the prostate, and infertility.
It is also possible that chlamydia can cause a reaction throughout the body that causes arthritis (joint pain). Other possible repercussions are conjunctivitis (pink eye), proctitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum from anal sex), open sores in the genital area, headache, fever, fatigue, lymphogranuloma venereum (swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin), and/or a rash on the soles of the feet or elsewhere.
How to avoid getting chlamydia in the throat
Be aware of the status of your new partner. We understand that this can be an uncomfortable conversation for some, so if you need help, check out our blog post for some tips.
Aside from talking to your partner about their status, you can also use protection, such as condoms. Not using protection is part of the reason why so many people end up with STDs like chlamydia. These precautions may not be seen as “fun,” but, if your sexual health is a concern, as it should be, the following are ways to protect yourself from getting oral chlamydia.
When engaging in oral sex on the penis, use a condom or another barrier method each and every time you have oral sex. When performing oral sex on the vagina or anus, use a dental dam or cut open a condom to make a square, then put it between the mouth and the partner’s vagina or anus.
Avoiding all forms of sex is really the only way to truly avoid getting an STD. If this doesn’t seem like a realistic route, you can lower your chances by being in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who is not infected with an STD.
Medically Reviewed by J. Frank Martin JR., MD on June 30, 2022
Secure and Confidential
STD testing services
The fastest results possbile - available in 1 to 2 days

Tagged
Categorized As
Author: Alexa Amador
Alexa graduated from a university in Atlanta with a B.A. in English and joined the STDcheck.com team in 2018. Before joining, she marketed and developed her own blog while working freelance for leading businesses. Having a robust skill set of research, writing, and editing has kept her busy and driven throughout both her academic and professional careers. Alexa became entangled in the sexual health business after coming from not only "abstinence-only" schooling but where the reproductive anatomy chapter was literally torn from her textbook. She realized how irresponsible it is for people to encourage ignorance about sexual health, especially to younger audiences, and so her passion for becoming part of the solution and educating the masses was born. When not writing for Exposed, Alexa enjoys taking vacations in the mountains with a good book and her dog, Nova.